MySQL基础应用
SQL 介绍
结构化查询语言
5.7 以后符合SQL92严格模式
通过sql_mode参数来控制
常用 SQL 分类
DDL:数据定义语言
DCL:数据控制语言
DML:数据操作语言
DQL:数据的查询语言
数据类型、表属性、字符集
数据类型
作用
保证数据的准确性和标准性
种类
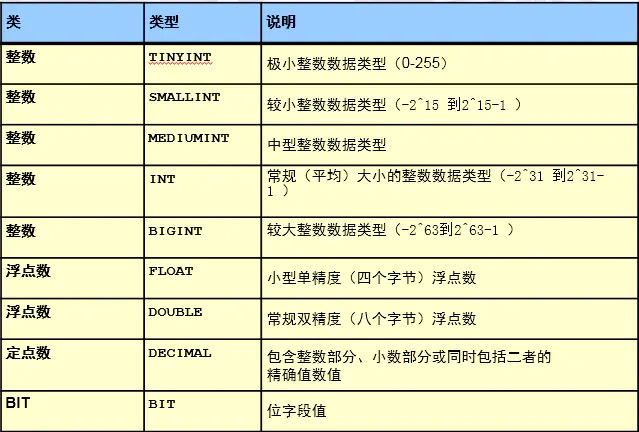
数值类型

tinyint : -128~127 int :-2^31~2^31-1 说明:手机号是无法存储到int的。一般是使用char类型来存储手机号字符类型

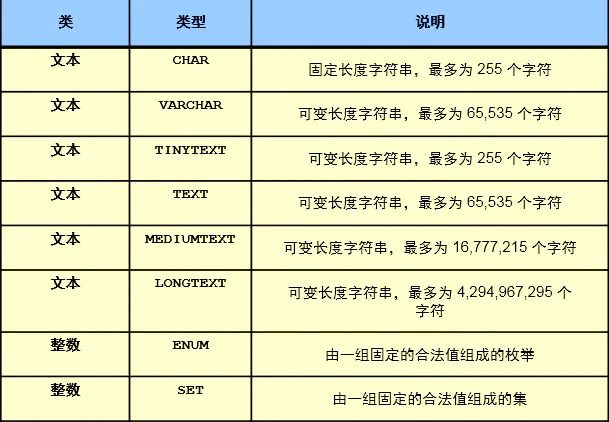
char(11) : 定长 的字符串类型,在存储字符串时,最大字符长度11个,立即分配11个字符长度的存储空间,如果存不满,空格填充。 varchar(11): 变长的字符串类型看,最大字符长度11个。在存储字符串时,自动判断字符长度,按需分配存储空间。 enum('bj','tj','sh'): 枚举类型,比较适合于将来此列的值是固定范围内的特点,可以使用enum,可以很大程度的优化我们的索引结构。时间类型

datatime 范围为从 1000-01-01 00:00:00.000000 至 9999-12-31 23:59:59.999999 timestamp 范围为从 1970-01-01 00:00:00.000000 至 2038-01-19 03:14:07.999999- 二进制类型

- 二进制类型
列属性
约束(一般建表时添加):
primary key: 主键约束
设置为主键的列,此列的值必须非空且唯一,主键在一个表中只能有一个
not null: 非空约束
列值不能为空,也是表设计的规范,尽可能将所有的列设置为非空,可以设置默认值0
unique key: 唯一键
列值不能重复
unsigned: 无符号
针对数字列,非负数
# 其他属性:
key: 索引
可以在某列上建立索引,来优化索引,一般是根据需要后添加
default: 默认值
列中,没有录入值时,会自动使用default的值填充
auto_increment: 自增长
针对数字列,顺序的自动填充数据(默认是从1开始,将来可以设置起始点和偏移量)
comment: 注释
表属性
存储引擎:
InnoDB(默认的)
字符集和排序规则:
utf8
utf8mb4
字符集
show charset; # 查看 mysql 支持的所有字符集
utf8: 3 个字节
utf8mb4: 4 个字节,支持 emoji
DDL 的应用
库定义
创建数据库
建库规范: 1.库名不能有大写字母 2.建库要加字符集 3.库名不能有数字开头 4. 库名要和业务相关 建库标准语句 create database test charset utf8mb4 collate utf8mb4_bin;删除
# 生产中禁止 drop database school;修改
# 创建一个没有设置字符集的库 create database school; # 如果是已经创建好的库的查看建库语句 show create database school; # 修改字符集 alter database school charset utf8mb4 collate utf8mb4_bin; # 注意:修改字符集,修改后的字符集一定是原字符集的严格超集(从小往大,不能从大往小)查询(属于 DQL)
# 查看所有库 show databases; # 查看库的建库语句 show create database test;
表定义
创建表
建表规范: 1. 表名小写 2. 不能是数字开头 3. 注意字符集和存储引擎 4. 表名和业务有关 5. 选择合适的数据类型 6. 每个列都要有注释 7. 每个列设置为非空,无法保证非空,用0来填充 格式: create table stu( 列1 属性(数据类型、约束、其他属性) , 列2 属性, 列3 属性 ) 创建一个学生表: use school; create table stu( id int not null primary key auto_increment comment '学号', sname varchar(255) not null comment '姓名', sage tinyint unsigned not null default 0 comment '年龄', sgender enum('m','f','n') not null default 'n' comment '性别', sfz char(18) not null unique comment '身份证', intime timestamp not null default now() comment '入学时间' ) engine=innodb charset= utf8mb4 comment '学生表'; show tables; # 查看是否创建成功 desc stu; # 查看表结构信息 show create table stu; # 查看建表语句修改表
# 在stu表中添加qq列 alter table stu add qq varchar(20) not null unique comment 'qq号'; # 在sname后加微信列 alter table stu add wechat varchar(20) not null unique comment '微信号' after sname; # 在id列前面加一个新列的num alter table stu add num int not null comment '数字' first; # 修改sname数据类型 alter table stu modify sname varchar(128) not null; # 将sgender该为sex 数据类型改为char类型 alter table stu change sgender sex char(1) not null default 'n'; # 删除刚才添加的列 alter table stu drop num; alter table stu drop qq; alter table stu drop wechat;查询表属性(DQL)
use school; show tables; desc stu; show create table stu; create table test like stu; # 创建一个和stu表结构一样的test表删除表
drop table stu;
DCL 的应用
用户的授权和权限的回收
grant
revoke
DML 的应用
对表中数据的增删改
insert
# 标准插入语句
insert into stu(id,sname,sage,sex,sfz,intime)
values
(1,'zhangsan',18,'m','110101199003070353',now());
select * from stu; # 查看stu表内数据
# 省事写法
insert into stu
values
(2,'lisi',19,'m','220101145664070363',now());
# 针对性录入数据
insert into stu(sname,sfz)
values('wangwu','33452982337621');
# 同时录入多行数据
insert into stu(sname,sfz)
values
('tiansha','4324654324312'),
('aaa','321435212354154'),
('lxx','556652353265326');
update
select * from stu;
update stu set sname='lxx2' where id=9;
select * from stu;
# update语句必须要加where
delete
delete from stu where id=9;
# 全表删除
DELETE FROM stu
truncate table stu;
区别:
delete: DML操作, 是逻辑性质删除,逐行进行删除,速度慢
truncate: DDL操作,对与表段中的数据页进行清空,速度快
# 伪删除
1.添加状态列
ALTER TABLE stu ADD state TINYINT NOT NULL DEFAULT 1 ;
SELECT * FROM stu;
2. UPDATE 替代 DELETE
UPDATE stu SET state=0 WHERE id=8;
3. 业务语句查询
SELECT * FROM stu WHERE state=1;
DQL 的应用(select)
作用: 获取 MySQL 中的数据行
单独使用
-- select @@xxx 查看系统参数
SELECT @@port; # 查看数据库软件的端口
SELECT @@basedir; # 查看数据库软件目录
SELECT @@datadir; # 查看数据库数据目录
SELECT @@socket; # 查看数据库socket文件位置
SELECT @@server_id; # 查看server_id号
show variables like '%innodb%';
-- select 函数();
SELECT NOW();
SELECT DATABASE();
SELECT USER();
SELECT VERSION();
SELECT CONCAT("hello world");
SELECT CONCAT(USER,"@",HOST) FROM mysql.user;
SELECT GROUP_CONCAT(USER,"@",HOST) FROM mysql.user;
单表查询
SQL92 标准的使用语法
select 语法执行顺序
select开始 ----> from子句 ----> where子句 ----> group by子句 ----> select后执行条件 ----> having子句 ----> order by子句 ----> limit
单表环境准备
# 如果下面的失效了在该网站下载, https://dev.mysql.com/doc/index-other.html
wget https://klcc-img-1251900471.cos.ap-chengdu.myqcloud.com/sql/world.sql
mysql -uroot -p1 < world.sql
mysql -uroot -p1 -e 'show databases;'
# 查看表
show tables from world;
city
country
countrylanguage
# 查看表结构
desc city;
FROM
use world;
select * from city; # 适合表数据行较少的,生产中较少使用,会造成数据库压力过大
# 查询name 和 population的所有值
select name,population from world.city;
WHERE
# where 配合 等值查询(=)
# 查询 city 表中,中国城市信息
select * from world.city where countrycode='CHN';
# where 配合 不等值查询(> >= < <= <>)
# 查询世界人口小于100人的城市
select * from world.city where population<100;
# 查询世界人口大于10000000的城市
select * from world.city where population > 10000000;
# where 配合 模糊查询(like)
# 查询国家代号是 C 开头的城市
select * from world.city where CountryCode like 'C%'; # 不要出现 % 在前面的情况, 效率低,不走索引
# 匹配符号
# %:匹配任意个数任意字符
# _:匹配单个个数任意字符
# where 配合 逻辑连接符查询(and or)
# 查询城市人口在10000到20000之间的城市
select * from world.city where population >= 10000 and population <= 20000;
select * from world.city where population between 10000 and 20000;
# 查询中国或美国的城市信息
select * from world.city where CountryCode='CHN' or CountryCode='USA';
select * from world.city where CountryCode in ('CHN', 'USA');
# distinct: 去重复
select countrycode from city;
select distinct(countrycode) from city;
# 聚合
union # 如果结果有重复项会自动去重复
union all # 如果有重复项不会去重复
# 这条语句性能比上面两条语句高
select * from world.city where CountryCode='CHN'
union all
select * from world.city where CountryCode='USA';
group by配合聚合函数应用
根据 by 后面的条件进行分组,方便统计,by 后面跟一个列或多个列
常用聚合函数
max() # 最大值 min() # 最小值 avg() # 平均值 sum() # 总和 count() # 个数 group_concat() # 列转行
# 统计每个国家的总人口
select CountryCode,sum(population) from world.city group by CountryCode;
# 统计每个国家 的城市个数
select CountryCode,count(Name) from world.city group by CountryCode;
# 统计并显示每个国家的省名字列表
select CountryCode,group_concat(district) from world.city group by CountryCode;
# 统计中国每个省的城市列表
select district, group_concat(Name) from world.city where CountryCode='CHN' group by district;
# 统计中国每个省的总人口数
select district,sum(population) from world.city where CountryCode='CHN' group by district;
having
# 统计中国每个省的总人口数,只打印总人口数小于1000000的省
select district,sum(population) from world.city where CountryCode='CHN' group by district having sum(population) < 1000000;
# having 后的条件是不走索引的,可以进行一些优化手段处理
order by
实现先排序, by 后添加条件列
# 统计中国每个省的总人口数并从小到大排序
select district,sum(population) from world.city where CountryCode='CHN' group by district order by sum(population);
# 统计中国每个省的总人口数并从大到小排序
select district,sum(population) from world.city where CountryCode='CHN' group by district order by sum(population) desc;
# 查询中国所有的城市,并以人口数降序排序
select Name, population from world.city where CountryCode='CHN' order by population desc;
limit
# 统计中国每个省的总人口数并从大到小排序只显示前5个
select district,sum(population) from world.city where CountryCode='CHN' group by district order by sum(population) desc limit 5;
# 统计中国每个省的总人口数并从大到小排序,显示第6-第10个
# 第一种
select district,sum(population)
from world.city
where CountryCode='CHN'
group by district
order by sum(population) desc
limit 5, 5;
# 第一个5代表跳过前五行, 第二个5表示再显示5行
# 第二种
select district,sum(population)
from world.city
where CountryCode='CHN'
group by district
order by sum(population) desc
limit 5 offset 5;
# 第一个5代表显示5行, offset代表偏移五行,跳过前五行
多表连接查询
将来要查询的数据,是来自于多张表时,可以用多表连接
环境准备
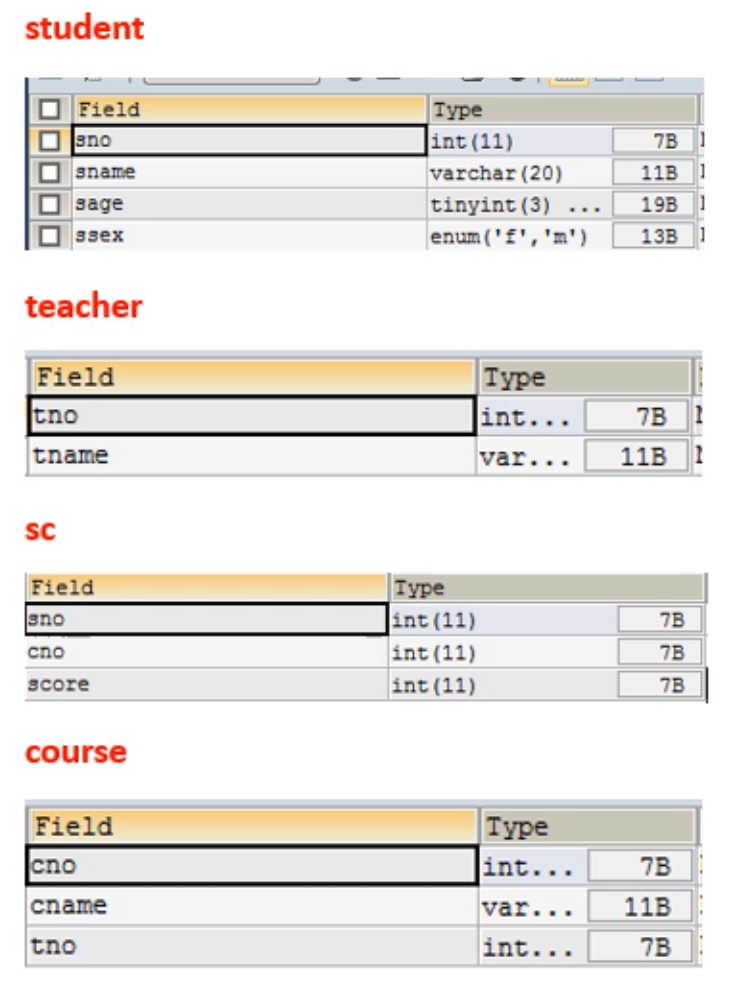
表结构:
use school
student :学生表
sno: 学号
sname:学生姓名
sage: 学生年龄
ssex: 学生性别
teacher :教师表
tno: 教师编号
tname:教师名字
course :课程表
cno: 课程编号
cname:课程名字
tno: 教师编号
score :成绩表
sno: 学号
cno: 课程编号
score:成绩
# 构建表
create database school charset utf8mb4;
use school;
create table student(
sno int not null primary key auto_increment comment '学号',
sname varchar(20) not null comment '姓名',
sage tinyint unsigned not null comment '年龄',
ssex enum('f','m') not null default 'm' comment '性别'
) engine=innodb charset=utf8;
create table teacher(
tno int not null primary key comment '教师编号',
tname varchar(20) not null comment '教师姓名'
) engine=innodb charset=utf8;
create table course(
cno int not null comment '课程编号',
cname varchar(20) not null comment '课程名字',
tno int not null comment '教师编号'
) engine=innodb charset=utf8;
create table sc(
sno int not null comment '学号',
cno int not null comment '课程编号',
score int not null comment '成绩'
) engine=innodb charset=utf8;
# 插入数据
INSERT INTO student(sno,sname,sage,ssex)
VALUES (1,'zhang3',18,'m');
INSERT INTO student(sno,sname,sage,ssex)
VALUES
(2,'zhang4',18,'m'),
(3,'li4',18,'m'),
(4,'wang5',19,'f');
INSERT INTO student
VALUES
(5,'zh4',18,'m'),
(6,'zhao4',18,'m'),
(7,'ma6',19,'f');
INSERT INTO student(sname,sage,ssex)
VALUES
('oldboy',20,'m'),
('oldgirl',20,'f'),
('oldp',25,'m');
INSERT INTO teacher(tno,tname) VALUES
(101,'oldboy'),
(102,'hesw'),
(103,'oldguo');
DESC course;
INSERT INTO course(cno,cname,tno)
VALUES
(1001,'linux',101),
(1002,'python',102),
(1003,'mysql',103);
DESC sc;
INSERT INTO sc(sno,cno,score)
VALUES
(1,1001,80),
(1,1002,59),
(2,1002,90),
(2,1003,100),
(3,1001,99),
(3,1003,40),
(4,1001,79),
(4,1002,61),
(4,1003,99),
(5,1003,40),
(6,1001,89),
(6,1003,77),
(7,1001,67),
(7,1003,82),
(8,1001,70),
(9,1003,80),
(10,1003,96);
SELECT * FROM student;
SELECT * FROM teacher;
SELECT * FROM course;
SELECT * FROM sc;
- 表之间的关系

内连接
# 查询人口数量小于100人的国家名,城市名,国土面积
select country.name,city.name,country.surfacearea
from
city join country
on city.countrycode=country.code
where city.population < 100;
# 查询oldguo老师和他教的课程名称
select teacher.tname,course.cname
from
teacher join course
on teacher.tno=course.tno
where teacher.tname='oldguo';
# 统计一下每门课程的总成绩
select course.cname,sum(sc.score)
from
course join sc
on course.cno=sc.cno
group by course.cname,course.cno;
# only_full_group_by错误
1.在select后面出现的列,不是分组条件,并且没有函数中出现
2.如果group by 后是主键列或者是唯一条件列
select course.cno,course.cname,sum(sc.score)
from
course join sc
on course.cno=sc.cno
group by course.cname;

# 查询oldguo老师教的学生姓名列表
select teacher.tname,group_concat(student.sname)
from
teacher join course
on teacher.tno=course.tno
join sc
on course.cno=sc.cno
join student
on sc.sno=student.sno
where teacher.tname='oldguo';
# 查询每个老师教的学生姓名列表
select teacher.tname,group_concat(student.sname)
from
teacher join course
on teacher.tno=course.tno
join sc
on course.cno=sc.cno
join student
on sc.sno=student.sno
group by teacher.tname;
# 查询oldguo老师教的不及格的学生姓名
select student.sname
from
teacher join course
on teacher.tno=course.tno
join sc
on course.cno=sc.cno
join student
on sc.sno=student.sno
where teacher.tname='oldguo' and sc.score < 60;
# 统计zhang3 学习了几门课
select student.sname,count(sc.cno)
from student
join sc
on student.sno=sc.sno
where student.sname='zhang3';
# 查询zhang3 学习的课程名称有哪些
select student.sname , group_concat(course.cname)
from student
join sc
on student.sno=sc.sno
join course
on sc.cno=course.cno
where student.sname='zhang3';
# 查询oldguo 所教课程的平均分数
select teacher.tname,avg(sc.score)
from teacher
JOIN course
ON teacher.tno=course.tno
JOIN sc
ON course.cno=sc.cno
WHERE teacher.tname='oldguo';
# 每位老师所教课程的平均分 并按平均分排序
select teacher.tname,course.cname, avg(sc.score)
from
teacher join course
on teacher.tno=course.tno
join sc
on course.cno=sc.cno
join student
on sc.sno=student.sno
group by teacher.tname,course.cname
order by avg(sc.score) desc;
# 查询所有老师所教学生不及格的信息
select student.sname,course.cname,sc.score
from
teacher join course
on teacher.tno=course.tno
join sc
on course.cno=sc.cno
join student
on sc.sno=student.sno
where sc.score < 60;
别名
# 表别名设置
# 查询所有老师所教学生不及格的信息
select d.sname,b.cname,c.score
from
teacher as a
join course as b
on a.tno=b.tno
join sc as c
on b.cno=c.cno
join student as d
on c.sno=d.sno
where c.score < 60;
# 列别名
select count(distinct(name)) from world.city;
select count(distinct(name)) as a from world.city;
外连接
左外连接和右外连接
# 内连接
select a.name,b.name, b.surfacearea
from world.city as a
join world.country as b
on a.countrycode=b.code
where a.population < 100;
# 左外连接
select a.name,b.name, b.surfacearea
from world.city as a
left join world.country as b
on a.countrycode=b.code
and a.population < 100;
# a.name的值全部出来了, b.name和b.surfacearea不满足的会用NULL填充
select a.name,b.name, b.surfacearea
from world.city as a
left join world.country as b
on a.countrycode=b.code
where a.population < 100;
# 右外连接
select a.name,b.name, b.surfacearea
from world.city as a
right join world.country as b
on a.countrycode=b.code
and a.population < 100;
information_schema.tables视图
介绍
1.虚拟库
2.开启数据库时产生的
3.不能被删除和修改
4.库中存储的是视图
5.此库中的视图也是不能被删除和修改的,只能select查询
作用
此库中的视图是用来,间接的查询数据库的"元数据"("基表"数据)
基表:数据是通过自动统计收集而来的.
基表:是不允许人为直接增\删\改\查的
必须通过:专用的DDL,DCL实现增\删\改,show语句和information_schema可以做查询
# 记录了:整个MySQL数据库中,所有的表的详细属性信息
desc information_schema.tables;
TABLE_SCHEMA ---->库名
TABLE_NAME ---->表名
ENGINE ---->引擎
TABLE_ROWS ---->表的行数
AVG_ROW_LENGTH ---->表中行的平均行(字节)
INDEX_LENGTH ---->索引的占用空间大小(字节)
CONCAT()函数使用
# 简单使用
select user, host from mysql.user;
select concat(user,"@",host) from mysql.user;
# 生产需求,下例子批量备份语句
相关使用
查询整个数据库中所有库和所对应的表信息
select table_schema,group_concat(table_name) from information_schema.tables group by table_schema;统计所有库下 的表个数
select table_schema,count(table_name) from information_schema.tables group by table_schema;查询所有 innodb 引擎的表及所在的库
select table_schema,table_name,engine from information_schema.tables where engine='innodb';统计 world 的数据库下每个表的行数
select table_name,table_rows from information_schema.tables where table_schema='world';统计 world 数据库下每张表的磁盘空间占用
select table_name,concat((TABLE_ROWS*AVG_ROW_LENGTH+INDEX_LENGTH)/1024," KB") as size_KB from information_schema.tables where table_schema='world';统计所有数据库的总磁盘空间占用
select table_schema,concat(sum(TABLE_ROWS*AVG_ROW_LENGTH+INDEX_LENGTH)/1024," KB") as Total_KB from information_schema.tables group by table_schema; mysql -uroot -p1 -e 'select table_schema,concat(sum(TABLE_ROWS*AVG_ROW_LENGTH+INDEX_LENGTH)/1024," KB") as Total_KB from information_schema.tables group by table_schema;'生成整个数据库下的所有表的单独备份语句
vim /etc/my.cnf secure-file-priv=/tmp # 在mysqld 标签下添加 systemctl restart mysqld.service # 重启数据库 模板语句: mysqldump -uroot -p123 world city >/tmp/world_city.sql 批量生成整个数据库的所有表的备份语句: select concat("mysqldump -uroot -p1 ",table_schema," ",table_name," > /bak/",table_schema,"_",table_name,".sql") from information_schema.tables;
常用 show 语句
show databases; # 查看所有数据库
show tables; # 查看当前库下的表
show tables from xxx; # 查看指定库下的表
show create database xxx; # 查看建库语句
show create table; # 查看建表语句
show grants for root@'localhost'; # 查看用户权限信息
show charset; # 查看所有字符集
show collation; # 校对规则
show engines; # 查看存储引擎支持情况
show status; # 看数据库的整体状态
show status like '%lock%' # 模糊查找数据库的状态
show variables; # 查看数据库所有变量情况
show variables like '%log%'; # 模糊查找相关数据库的变量情况
show full processlist; # 看数据库连接线程状态
show engine innodb status \G # 看innodb存储引擎总状态
show master status; # 主从复制中库信息
show slave status \G # 主从复制从库状态
show binary logs; # 可用的binlog文件名
show binlog events in ''; # binlog日志的事件信息
show relaylog events in ''; # 查看relaylog日志情况
select @@log_error; # 查看某个参数的定义信息
select now(); # 查看当前时间
select database(); # 查看当前use到的库
select user(); # 当前登录的用户